
The gel allows sound waves to travel back and forth between the transducer and the area under examination. The technologist applies a small amount of gel to the area under examination and places the transducer there. The same principles apply to sonar used by boats and submarines. The transducer sends out inaudible, high-frequency sound waves into the body and listens for the returning echoes. Some exams may use different transducers (with different capabilities) during a single exam. The transducer is a small hand-held device that resembles a microphone. Ultrasound machines consist of a computer console, video monitor and an attached transducer.
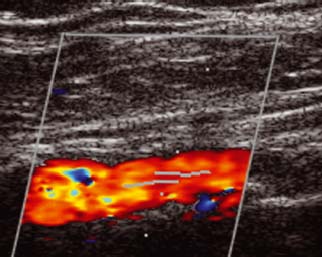
The major goal of carotid ultrasound is to screen patients for blockage or narrowing of their carotid arteries, which if present may increase their risk of having a stroke. The carotid ultrasound is most frequently performed to detect narrowing, or stenosis, of the carotid artery, a condition that substantially increases the risk of stroke. What are some common uses of the procedure? It allows the doctor to see and evaluate blood flow through arteries and veins in the body. The images can also show blood flowing through blood vessels.Īn ultrasound of the body's two carotid arteries, which are located on each side of the neck and carry blood from the heart to the brain, provides detailed pictures of these blood vessels and information about the blood flowing through them.Ī Doppler ultrasound study is usually an integral part of a carotid ultrasound examination.ĭoppler ultrasound is a special ultrasound technique that evaluates movement of materials in the body. Because ultrasound captures images in real-time, it can show the structure and movement of the body's internal organs. Ultrasound exams do not use radiation ( x-rays). A computer uses those sound waves to create an image. The probe collects the sounds that bounce back. High-frequency sound waves travel from the probe through the gel into the body. It uses a small probe called a transducer and gel placed directly on the skin. Ultrasound imaging is also called sonography.


It produces pictures of the inside of the body using sound waves.

Ultrasound imaging is a noninvasive medical test that helps physicians diagnose and treat medical conditions.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
